VDOM runtime 源码入门
— FE Tutorial, Front End Framework — 1 min read
Table of Contents
序
1. 核心部分小于 200 行
去掉 key diff 后真的很简单
2. 框架原理入门的入门
Go deeper 部分就是框架原理入门
3. 学习框架原理的起点
Go deeper 链接中的链接中的链接……
VNode
1[Virtual Node]2--------------3[DOM Node]用来找到两个帧之间不同的地方(diff),仅对不同的地方进行实际的 DOM 更新(patch),减少与 DOM 通信、回流重回等性能消耗
于是需要在真是的 DOM Node 上建立一层 VNode,用以描述帧的 DOM 结构
就是普通的 JS 对象,存在内存中,下一帧的 VNode 和当前帧的 VNode 进行比对,找到需要更新的地方,然后做相应处理
Vue 是一边 diff 一边 patch;React16 是先 diff 然后对要更新的地方做标记(render phase),之后在对标记过的地方进行 patch(commit phase)。实现的不同也决定了一些 feature 的不同
前两部分先不考虑组件,仅对应 DOM 结构的两种 VNode,标签(div、span……)和文本(#text)进行处理(对应 DOM 中 Element、Text、Comment 都继承于 Node 类型)
1{2 type,3 props,4 key, // key diff 用的5 node, // 宿主环境的元素(dom node……)6 parent, // parent VNode7 children, // VNode[],建立内部 VNode 树结构8}Diff
1div diff2 / \ diffChildren3 div div diff diff4 | | diffChildren diffChildren5hello world diff diff
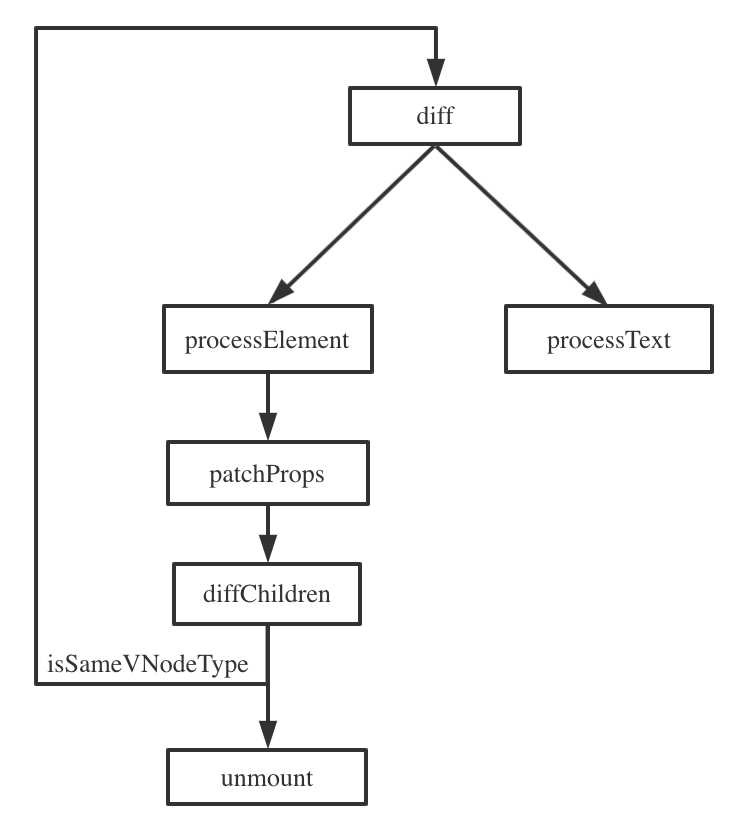
- 只对同级元素进行 diff(diffChildren)
- 两个不同类型的元素会产生出不同的树(isSameVNodeType)
- 开发者可以通过 key 来暗示哪些子元素在不同的渲染下能保持稳定(key diff)
key diff 位于 diffChildren 这里,是 diff 算法最难的地方,代码中我们简化了很多,详细的可以看 Go deeper 链接中的链接
Vue 使用的是递归式的 diff,React16 使用的是迭代式的 diff,区别在于递归式的不可打断,迭代式的可以打断,这也决定了两个框架 feature 的不同 代码中因为参考的是 Vue3 的源码,边 diff 边 patch,所以命名是 patch,但实际上做的是 diff + patch
Component
现在我们加入 Component 的 diff
1const hooksComponent = {2 patch(internals, { n1, n2, container }) {3 if (n1 == null) {4 const instance = n2.instance = {5 subTree: null,6 vnode: n2,7 update: () => {8 // this: extends hooksComponent9 const renderResult = this.render(instance.vnode.props) // 获取 render 的结果1011 instance.vnode.children = [renderResult] // 不考虑 Fragment,组件的子节点只有一个12 renderResult.parent = instance.vnode // 建立父子联系13 internals.patch(instance.subTree, renderResult, container) // 跟上一次结果进行 diff14 instance.subTree = renderResult // 存储这次结果,供下一次 patch 用15 },16 }17 } else {18 const instance = n2.instance = n1.instance19 instance.vnode = n220 }21 n2.instance.update()22 },2324 unmount(internals, { vnode, doRemove }) {25 vnode.children.forEach(c => unmount(c, doRemove))26 },2728 getNode(internals, { vnode }) {29 return vnode.instance.subTree.node30 }31}3233export const createHooksComponent = (render) => ({ ...hooksComponent, render }) // “继承“ patch、unmount 等方法现在的组件的更新是同步的,就是说比如一个 input,输入多少次就触发了多少次 diff,可以通过异步进行优化
1enqueueRender(n2.instance.update)State
组件的 State 我们通过 Hooks “钩”入
1const instance = n2.instance = {2 // ...3 hooks: {4 list: [],5 pendingEffects: [],6 },7 update: () => {8 currentHooksComponent = instance9 currentIndex = 010 // this: extends hooksComponent11 const renderResult = this.render(instance.vnode.props)12 currentHooksComponent = null13 // ...14 invokePendingEffects(instance)15 },16}1718function getHookState(index) {19 const { hooks } = currentHooksComponent20 if (index >= hooks.list.length) {21 hooks.list.push({});22 }23 return hooks.list[index];24}2526export function useEffect(effect, args) {27 const hookState = getHookState(currentIndex++);28 if (argsChanged(hookState.args, args)) {29 hookState.effect = effect;30 hookState.args = args;31 currentHooksComponent.hooks.pendingEffects.push(hookState);32 }33}两类 Reactivity 的处理方式:一种是以 Vue 为代表的 mutable + change tracking。即可变的数据结构,配合变更追踪,触发更新函数。另一种是以 React 为代表的 immutability + referential equality testing。即不可变的数据结构,配合反复执行的渲染函数,以及在函数执行过程中,通过数据的引用相等性判断,找出变更部分,只应用变化的部分到 UI 上。—— 工业聚:打破框架的范式之争